Introduction to PCOS
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS), also known as Polycystic Ovarian Disease (PCOD), is a common hormonal disorder that affects millions of women worldwide. It is one of the leading causes of hormonal imbalance and can have a significant impact on reproductive health, metabolism, and overall well-being.
What is PCOS?
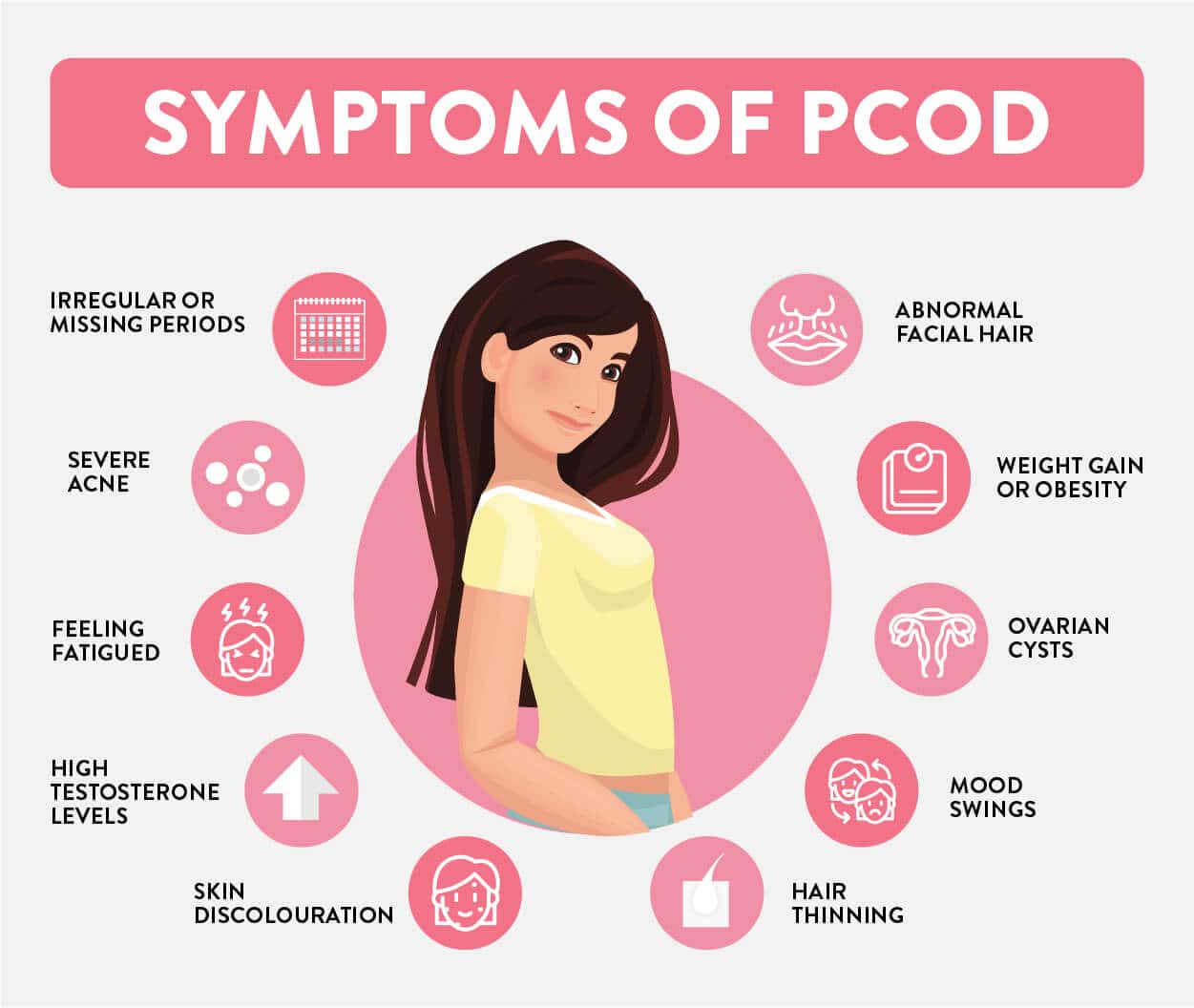
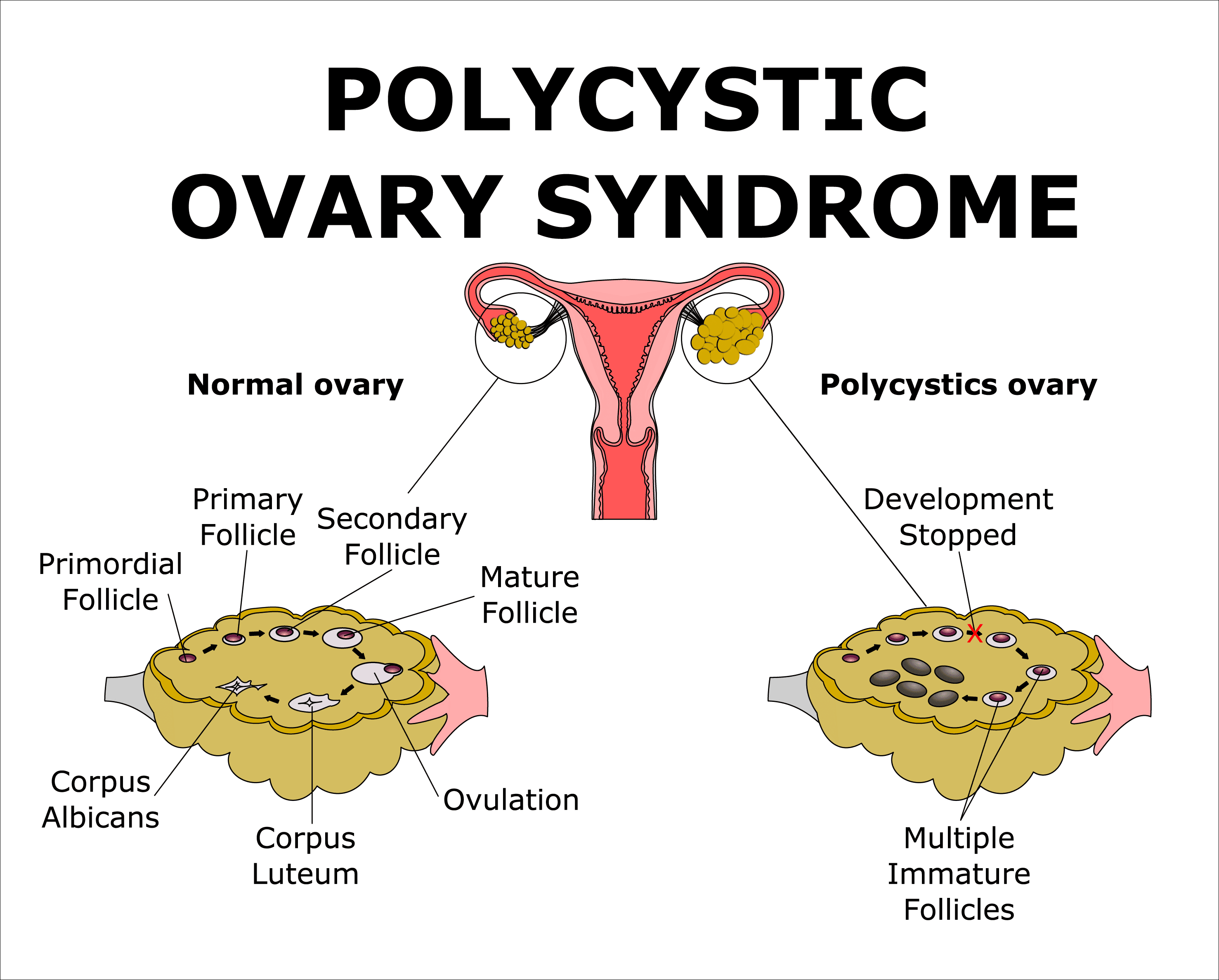
PCOS is a condition in which the ovaries produce higher-than-normal amounts of androgens (male hormones), leading to various symptoms. Despite its name, not all women with PCOS develop ovarian cysts. Instead, the syndrome is diagnosed based on a combination of symptoms, including irregular periods, excessive hair growth, acne, and difficulties with weight management.
Causes of PCOS
The exact cause of PCOS is unknown, but several factors contribute to its development:
- Hormonal Imbalance: Increased levels of androgens disrupt normal ovulation, leading to irregular menstrual cycles.
- Insulin Resistance: Many women with PCOS have insulin resistance, meaning their bodies do not use insulin effectively, which can lead to weight gain and an increased risk of diabetes.
- Genetic Factors: PCOS often runs in families, suggesting a genetic link.
- Inflammation: Chronic low-grade inflammation has been linked to higher androgen levels and PCOS symptoms.
Symptoms of PCOS
How is PCOS Diagnosed?
There is no single test to diagnose PCOS. Instead, doctors consider a combination of the following:
- Medical History & Symptoms: Reviewing menstrual patterns and signs of androgen excess.
- Physical Exam: Checking for visible symptoms such as excessive hair growth and acne.
- Blood Tests: Measuring hormone levels, insulin resistance, and lipid profiles.
- Ultrasound: Examining the ovaries for cysts and checking the thickness of the uterine lining.
Difference Between PCOS and Commonly Confused Diseases
PCOS shares symptoms with other conditions, leading to frequent misdiagnoses. Understanding the differences can help in getting the right treatment.
- PCOS vs. Hypothyroidism: Both conditions can cause weight gain, irregular periods, and fatigue. However, hypothyroidism is due to an underactive thyroid gland and is diagnosed through thyroid hormone tests, whereas PCOS involves high androgen levels and insulin resistance.
- PCOS vs. Cushing’s Syndrome: Cushing’s Syndrome is caused by excessive cortisol production and may lead to weight gain, acne, and menstrual irregularities, similar to PCOS. However, Cushing’s Syndrome also presents with symptoms like a rounded face, muscle weakness, and fragile skin, which are not common in PCOS.
- PCOS vs. Adrenal Hyperplasia: Congenital adrenal hyperplasia (CAH) can also cause excess androgen production, similar to PCOS. However, CAH is typically diagnosed at an early age and involves different enzyme deficiencies affecting steroid hormone production.
- PCOS vs. Ovarian Tumors: In rare cases, ovarian tumors can produce excess androgens, mimicking PCOS symptoms. Proper imaging and hormone tests can help differentiate between the two.
Managing PCOS
While there is no cure for PCOS, its symptoms can be managed through lifestyle changes, medications, and holistic approaches:
- Healthy Diet: Eating a balanced diet rich in whole foods, fiber, and lean proteins can help regulate insulin levels.
- Regular Exercise: Physical activity helps improve insulin sensitivity and manage weight.
- Stress Management: Practices like yoga, meditation, and mindfulness can support hormonal balance.
- Medical Treatment: Doctors may prescribe hormonal birth control, insulin-sensitizing drugs, or fertility treatments depending on individual needs. {However, in most cases you can manage by following above three}
The Importance of Awareness
PCOS is a lifelong condition that affects not only reproductive health but also cardiovascular and metabolic health. Raising awareness and seeking proper medical guidance can help women with PCOS lead healthier lives and reduce long-term health risks.
By understanding PCOS, women can take proactive steps to manage their symptoms and improve their quality of life.




No comments:
Post a Comment